

Step 1 (Preparations): Go through videos, resources, examples, and step by step exercises you find below in your own pace.It is an advantage if you know what a differential equation is. Prerequisites: Basic LabVIEW Programming. To understand how to set the PID values is outside the scope of this exercise but information on PID tuning is readily available from the web or textbooks on control.Video: LabVIEW in Automation - Control Systems in LabVIEW You can experiment with different set points as well as different PID values.Use the P, I and D values as shown in the front panel. Set the control temperature between T amb and T max that you measured earlier. Observe the temperature reading, is it giving the correct values? If yes, then you are ready to set the temperature and put the heater under PID Control.If you observe the LED intensity changing,your circuit is connected OK. When you change the manual heater setting dial, the gauge output and the LED intensity will change. This will set the heater output to manual override. As the load resistor is not designed to be a heating element, you may not be able to heat up the area around the thermistor to above 38 C (this will depend on the environment of the room you are working in).If you have connected the optional LED, the LED intensity should also change as you adjust the heater output. One way to check the your circuit is to observe the temperature when you change the PWM output.
Note that setting the PWM output to 0 turns off the heater and 100 turns on the heater completely.
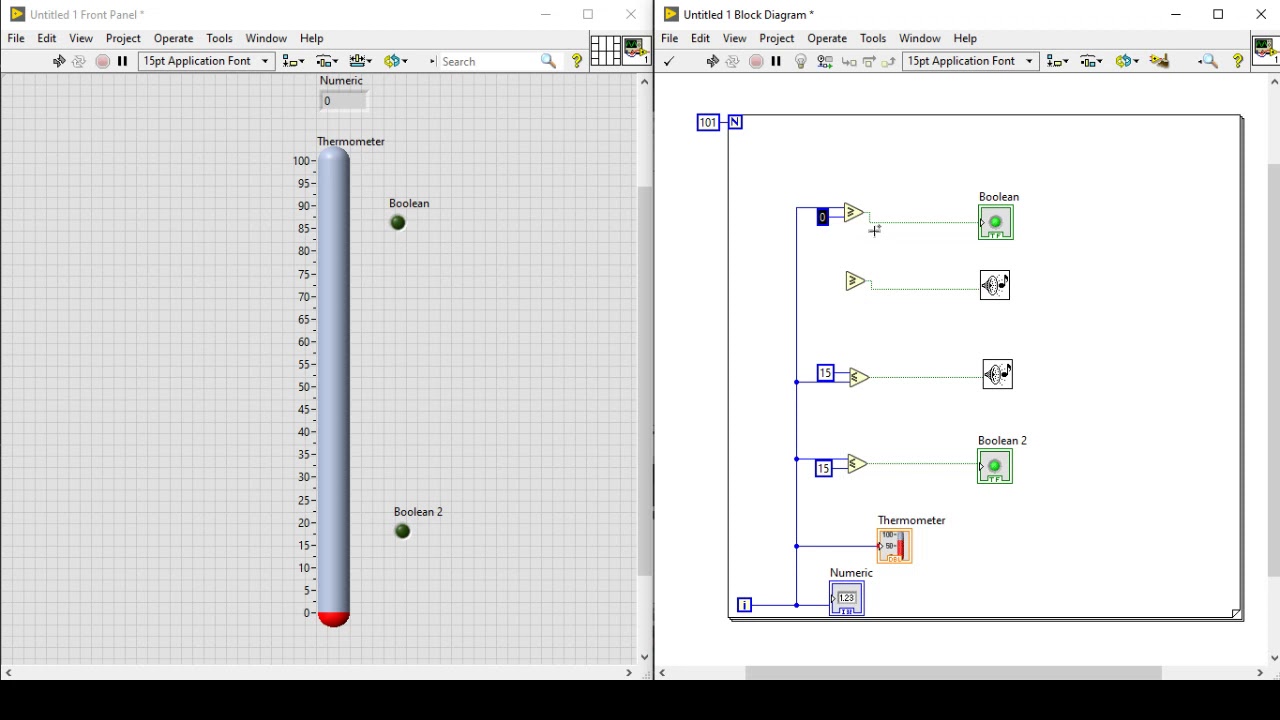
LabVIEW Front Panel LabVIEW Block Diagram


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
